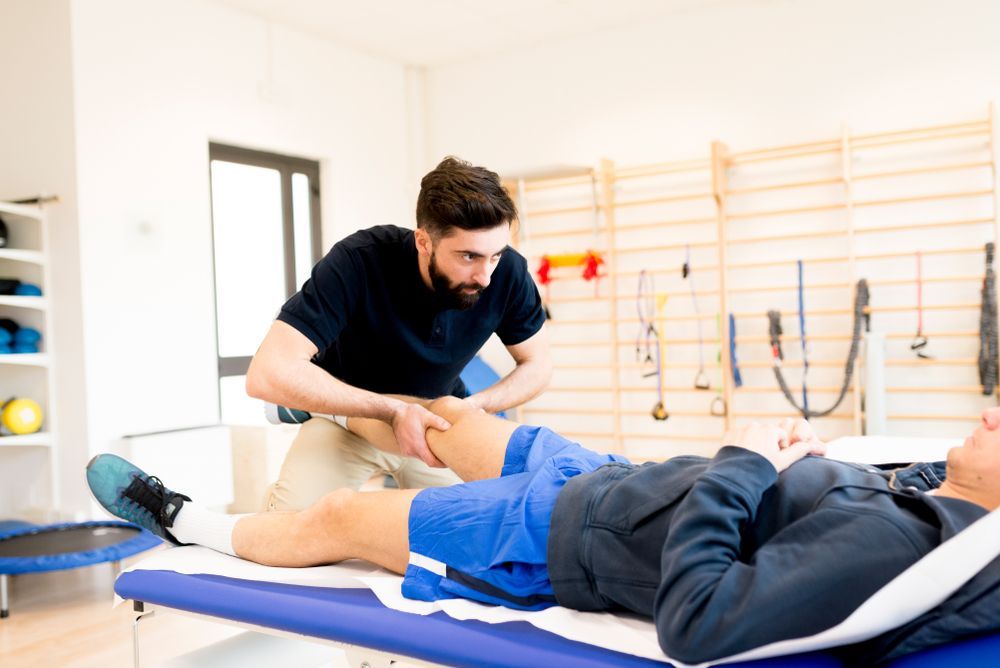
Exploring Manual Therapy in Physiotherapy: A Comprehensive Approach to Spinal Dysfunctions
- By rozsa@physio-medicine.co.uk
- •
- 30 Jan, 2024
- •
Introduction:
Physiological Effects of Manual Therapy on Human Tissues:
Increased Joint Range of Motion: Gentle mobilization techniques aim to enhance joint flexibility, promoting a wider range of motion in the spine.
Synovial Fluid Circulation:Mobilization stimulates the production and circulation of synovial fluid, aiding in joint lubrication and nourishment.
Spinal Manipulation:
Pain Modulation: Manipulative techniques can influence pain receptors, potentially reducing pain perception in individuals with spinal dysfunctions.
Facilitation of Joint Function: Manipulation may restore normal joint mechanics, improving overall joint function.
Soft Tissue Effects:
Muscle Relaxation: Manual therapy can alleviate muscle tension and spasms, contributing to improved flexibility and reduced discomfort.
Improved Blood Circulation: Enhanced circulation helps deliver oxygen and nutrients to soft tissues, supporting the healing process.
Procedure Of Manual Therapy:
Physiotherapists conduct a thorough assessment to identify specific spinal dysfunctions and determine the most appropriate manual therapy techniques.
Patient Positioning:
Patients are positioned in a way that facilitates access to the targeted spinal area, ensuring a comfortable and effective treatment session.
Technique Application:
Mobilization involves gentle, repetitive movements applied within the natural range of motion.
Manipulation comprises precise, controlled thrusts to restore joint function.
Potential Side Effects of Manual Therapy:
While manual therapy is generally safe, some individuals may experience:
- Temporary Soreness: Mild soreness or discomfort immediately following treatment is not uncommon.
- Rare Adverse Reactions: In rare cases, individuals may experience headaches or increased pain. It's crucial for practitioners to carefully assess patients before applying manual therapy.
Who Can Benefit From Manual Therapy
Individuals with spinal conditions such as herniated discs, facet joint dysfunction, or spinal stenosis.
Rehabilitation:
Patients recovering from surgeries or injuries benefit from manual therapy to restore normal function.
Chronic Pain Management:
Those dealing with chronic back pain often find relief through manual therapy interventions.
Preventive Care:
Athletes and individuals seeking to prevent spinal issues can benefit from regular manual therapy sessions.
Conclusion