Differences Between Osteopaths and Physiotherapists
- By Adbullah .
- •
- 24 Jul, 2023
- •

Definitions and Background
Osteopathy is a holistic branch of alternative medicine that emphasizes the interrelation between the body's structure and function. Osteopaths believe that the body has the inherent ability to heal itself when provided with the right conditions. They use manual techniques to diagnose and treat various health issues, focusing on the musculoskeletal system.
Physiotherapists:
Physiotherapy, also known as physical therapy, is a healthcare profession primarily concerned with improving and restoring physical function and mobility. Physiotherapists employ various techniques, exercises, and modalities to address a wide range of conditions, from orthopedic injuries to neurological disorders.
Education and Training
Osteopaths typically complete a rigorous undergraduate degree in osteopathy, followed by several years of postgraduate training. They receive comprehensive education in anatomy, physiology, biomechanics, and manual therapy techniques. The curriculum also includes clinical practice and hands-on experience.
Physiotherapists:
Physiotherapists must obtain a bachelor's degree in physiotherapy or a related field. Their education encompasses a broad range of medical sciences, including anatomy, kinesiology, neurology, and therapeutic exercises. Like osteopaths, physiotherapists gain clinical experience through internships and practical training.
Treatment Approaches
Osteopathic treatment revolves around the belief that the body's structure plays a significant role in its overall health. Osteopaths use a hands-on approach to identify and address restrictions, imbalances, and dysfunctions in the musculoskeletal system. They employ techniques such as manipulation, mobilization, and soft tissue therapy to enhance circulation, reduce pain, and improve the body's self-regulatory mechanisms.
Physiotherapists:
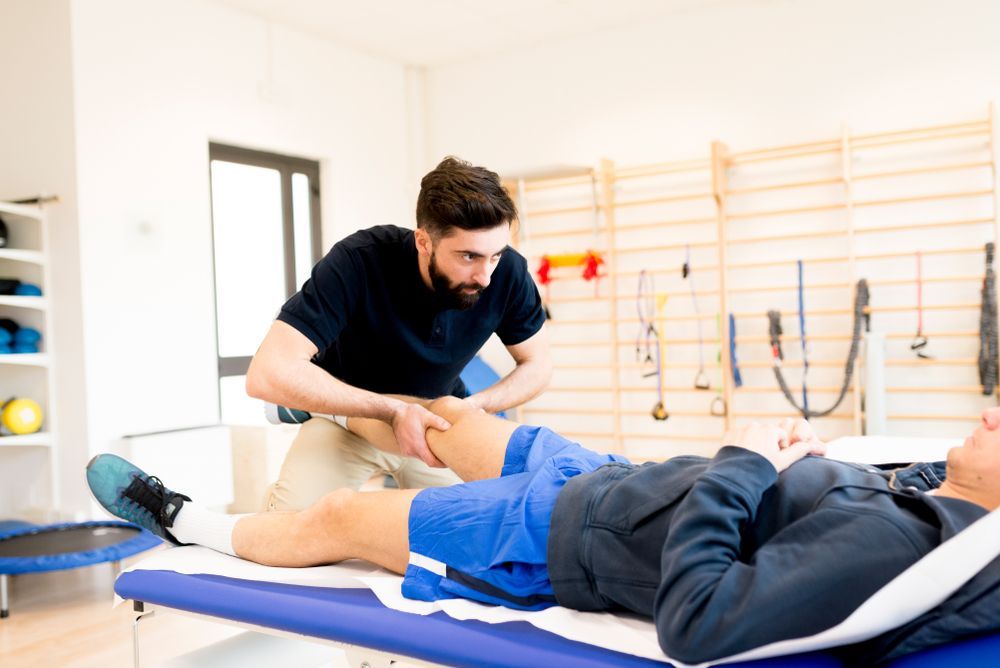
Physiotherapy focuses on promoting mobility, function, and independence. Physiotherapists use evidence-based approaches to create personalized treatment plans for their patients. These may include therapeutic exercises, electrotherapy, ultrasound, and heat or cold applications. They aim to strengthen muscles, improve range of motion, and facilitate the body's natural healing processes.
Scope of Practice
Osteopaths often take a broader perspective when assessing patients. They consider not only the site of pain but also how other areas of the body may be contributing to the issue. Osteopathic treatment can be beneficial for musculoskeletal problems, but some practitioners may also offer complementary therapies for general wellness.
Physiotherapists:
Physiotherapists have a diverse scope of practice and can work with patients of all ages and conditions. They specialize in orthopedic, neurological, cardiopulmonary, and sports-related rehabilitation. Physiotherapy is commonly employed after surgery or injury to aid in recovery and enhance physical function.
Focus on Holism
Holism is a fundamental principle in osteopathy, emphasizing the interconnectedness of the body's systems and the importance of treating the whole person rather than just the symptoms. Osteopaths often consider lifestyle, diet, and emotional well-being as part of their treatment approach.
Physiotherapists:
While physiotherapists do consider the whole person during treatment, their primary focus is on addressing the physical aspect of the condition. They concentrate on restoring functional movement and minimizing pain or discomfort.
Conditions Treated
Osteopaths commonly treat musculoskeletal issues, including back and neck pain, joint pain, and sports injuries. They may also assist with conditions like headaches, migraines, and digestive disorders.
Physiotherapists:
Physiotherapists treat a wide range of conditions, including sprains, strains, fractures, arthritis, stroke, spinal cord injuries, and post-surgical rehabilitation.
In summary, both osteopaths and physiotherapists play crucial roles in the healthcare system, focusing on restoring and improving physical function. Osteopaths use manual techniques to address musculoskeletal issues and adopt a holistic approach to treatment, considering the interconnectedness of the body. On the other hand, physiotherapists employ a wide range of evidence-based techniques and exercises to target specific conditions and promote mobility.
When choosing between osteopathy and physiotherapy, it's essential to consider the nature of the health issue and the treatment approach that aligns best with your needs and beliefs. Both professions can contribute significantly to your overall health and well-being, helping you regain control over your body and lead a fulfilling life. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific condition.